
Dermoscopy of Pigmented Spitz and Reed Nevi Dermatology JAMA Dermatology The JAMA Network
Reed naevus; Meyerson naevus is a naevus affected by a halo of eczema / dermatitis. Halo naevus or Sutton naevus has a white halo around the mole. The mole gradually fades away over several years. Spitz naevus or epithelioid cell naevus is a pink (classic Spitz) or brown (pigmented Spitz) dome-shaped mole that arises in children and young adults.

Dermoscopy Made Simple Reed Nevus
The Spitz naevus (syn. spindle cell naevus, epithelioid cell naevus, juvenile melanoma) is a variant of a compound naevus and is most commonly seen in children . The pigmented spindle cell naevus of Reed (PSCNOR) is a variant of a compound or occasionally a junctional naevus. There is debate as to whether the PSCNOR is an entity in its own.

Figure 1 from Pigmented Spindle Cell Nevus of Reed of the Eyelid Semantic Scholar
The Reed Nevus or pigmented spindle cell nevus (PSCN) was first described by Reed et al. in 1975 . Its designation as a separate entity vs. a SN variant remains controversial, but is currently considered by the 2018 WHO Classification to be a "distinct variant of Spitz naevus.".

Dermoscopy of Pigmented Spitz and Reed Nevi The Starburst Pattern Dermatology JAMA
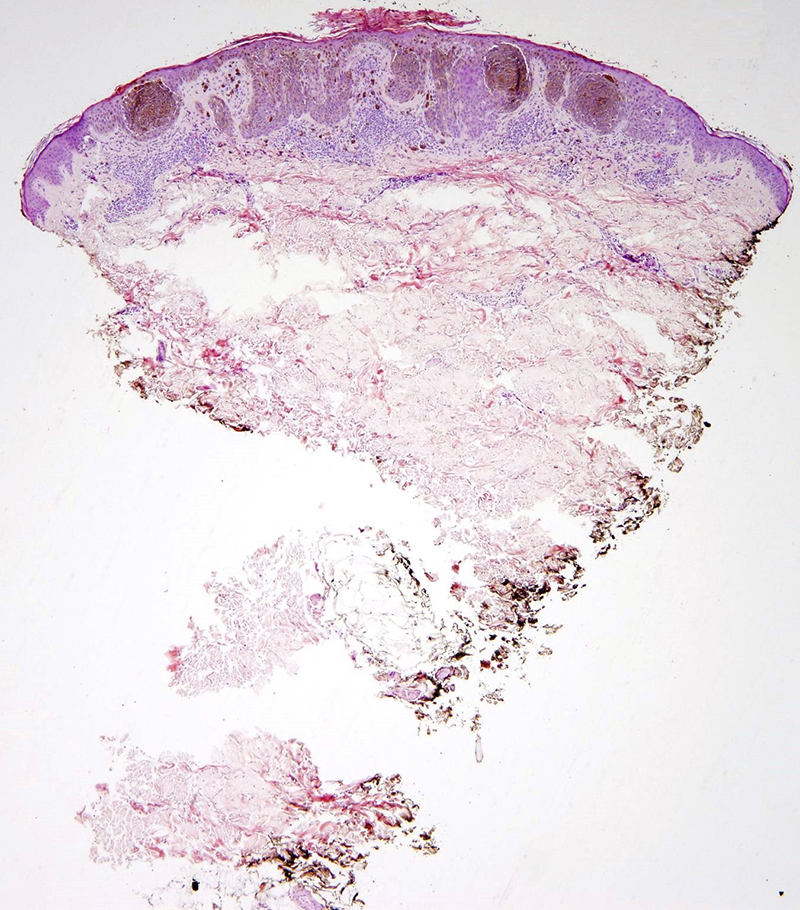
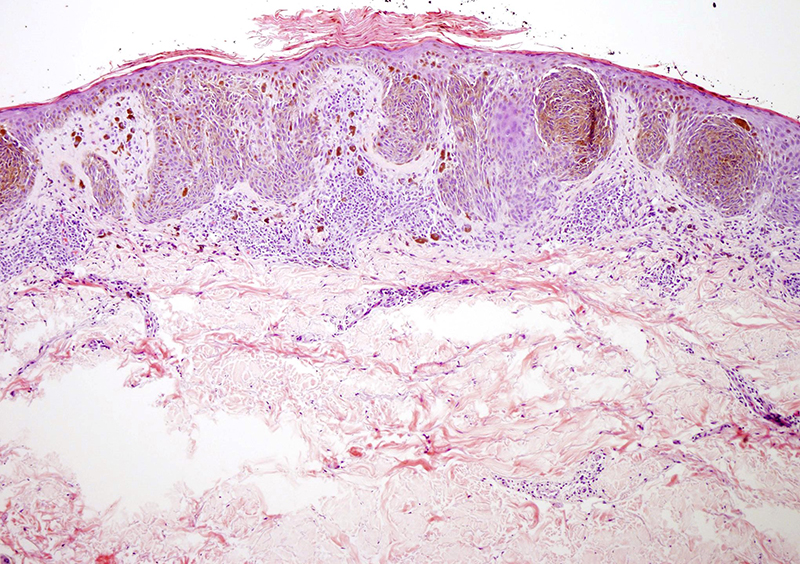
Reed nevus is composed histologically of elongated spindle-shaped and nevoid cells with a benign biologic behavior. Histopathological features in common with Spitz nevi and in contrast with malignant melanoma include a relatively small size, lesion symmetry, uniformity of cell type, good circumscription, and maturation of cells from superficial.

Dermpath Made Simple Neoplastic Spitz Nevus and Reed Nevus
'Nevus, Reed' published in 'Dermatopathology' Pigmented spindle cell nevus is a sharply demarcated and symmetrical melanocytic lesion characterized by a florid and cellular junctional component and marked melanin pigmentation (Fig. 1).The junctional aspect is composed of large and prominent nests containing uniform, spindled melanocytes arranged in fascicles with a characteristic vertical.

Nevus definition, types, diagnosis & nevus treatment
Update on dermoscopy of Spitz/Reed naevi and management guidelines by the International Dermoscopy Society Br J Dermatol. 2017 Sep;177(3):645-655. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15339.. Nevus, Epithelioid and Spindle Cell / pathology Nevus, Epithelioid and Spindle Cell / therapy*.

Reed Nevus (Pigmented Spindle Cell Nevus) in an 11MonthOld Japanese Infant
However, to date, many textbooks or atlases of dermatology or histopathology assert that Reed nevus is a variant of Spitz nevus [4,6,21-25]. According to Argenziano et al, a dermatopathologic distinction between pigmented Spitz and Reed nevus is difficult, not reproducible and maybe clinically useless.
Nevo de Reed. Diagnóstico dermatoscópico de un caso PIELL Latinoamericana
A Reed naevus is a very dark pigmented melanocytic naevus with spindle-shaped dermal melanocytes on histology. It was first reported by dermatologist Richard Reed in 1975. It is also known as a spindle cell naevus. Reed naevus is sometimes classified as a kind of Spitz naevus; the spindle-shaped cells of the Reed naevus may coexist with the.
Pigmented Spindle Cell Nevus of Reed Dermatopathology
A Reed nevus is a dark brown or black, raised, dome-shaped mole that most often affects women. These moles can grow quickly and may be mistaken for melanoma. These moles can grow quickly and may.

Dermpath Made Simple Neoplastic Spitz Nevus and Reed Nevus
Spitz naevus is classified as classic, pigmented, or spindle cell tumour of Reed. The classic Spitz naevus is typically a dome-shaped red, reddish-brown papule. A pigmented Spitz naevus is a tan or brown papule or nodule. A pigmented spindle cell tumour of Reed is a bluish or black papule. There are clinical features in common for all three.

Dermpath Made Simple Neoplastic Spitz Nevus and Reed Nevus
In contrast to Spitz nevus, the indicators of a congenital origin of Reed nevus are poor. The outstanding reports on agminated or systematized Reed nevi, or Reed nevus as constituent of a combined nevus, rather suggest a histogenetic event compatible with what is regarded to be a truly acquired melanocytic nevus and might represent another clue.

Naevus van Reed (pigmented spindle cell nevus)
Differential diagnosis of Spitz and Reed naevi. The differential diagnosis of Spitz and Reed naevi includes acquired melanocytic naevi, blue naevi and melanoma.. Spitz tumours with kinase fusions. It has recently been shown that spitzoid neoplasms harbour kinase fusions of ROS1 (17%), NTRK1 (16%), ALK (10%), BRAF (5%) and RET (3%) in a mutually exclusive pattern.

Evolution of Reed Nevi Dermoscopic Pattern in Childhood Dermatology JAMA Dermatology JAMA
Symmetric with cytologic maturation. Nests and fascicles of spindled melanocytes along dermoepidermal junction and within dermal papillae. May be junctional or compound. Expansive, not infiltrative growth pattern. Extends no deeper than reticular dermis. Nevus cells typically contain abundant melanin pigment, may be associated with melanophages.
Pigmented Spindle Cell Nevus of Reed Dermatopathology
The histopathologic distinction between Spitz nevus and Reed nevus is often matter of great debate. Nowadays, we distinguish two clinical variants of SN, the classical and the pigmented types, the latter include Reed nevus. The most important issue of SN is their propensity to mimic melanoma clinically, dermatoscopically and histopathologicallly.

Dermatoscopic patterns of Reed nevus. Starburst pattern in which black,... Download Scientific
Pigmented spindle cell nevus is a benign melanocytic lesion that was initially described in 1975 by Reed et al. It is generally found on the trunk or lower extremities of young women. Most authors consider it to be a variant of Spitz nevus. The main concern with these lesions remains their propensity to mimic melanoma both clinically and histologically.

Starburst dermoscopic pattern of Reed nevus Download Scientific Diagram
The clinical-dermatoscopic-histological correlation of excised Spitz/Reed nevi revealed overlapping histopathological features among lesions displaying distinct dermatoscopic patterns ( Figures 1 - 3 ). Among lesions with histopathological atypia (16/47, 34.0%), all dermatoscopic patterns were represented, although the atypical/multicomponent.